Novel glucosinolate metabolism in larvae of the leaf beetle Phaedon cochleariae
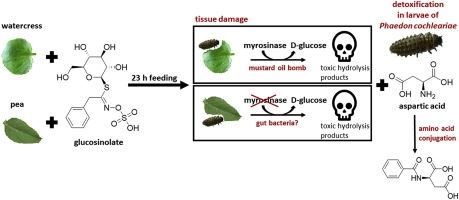
Plants of the Brassicales are defended by a binary system, in which glucosinolates are degraded by myrosinases, forming toxic breakdown products such as isothiocyanates and nitriles. Various detoxification pathways and avoidance strategies have been found that allow different herbivorous insect taxa to deal with the glucosinolate-myrosinase system of their host plants. Here, we investigated how larvae of the leaf beetle species Phaedon cochleariae (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), a feeding specialist on Brassicaceae, cope with this binary defence. We performed feeding experiments using leaves of watercress (Nasturtium officinale, containing 2-phenylethyl glucosinolate as major glucosinolate and myrosinases) and pea (Pisum sativum, lacking glucosinolates and myrosinases), to which benzenic glucosinolates (benzyl- or 4-hydroxybenzyl glucosinolate) were applied. Performing comparative metabolomics using UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS, N-(phenylacetyl) aspartic acid, N-(benzoyl) aspartic acid and N-(4-hydroxybenzoyl) aspartic acid were identified as major metabolites of 2-phenylethyl-, benzyl- and 4-hydroxybenzyl glucosinolate, respectively, in larvae and faeces. This suggests that larvae of P. cochleariae metabolise isothiocyanates or nitriles to aspartic acid conjugates of aromatic acids derived from the ingested benzenic glucosinolates. Myrosinase measurements revealed activity only in second-instar larvae that were fed with watercress, but not in freshly moulted and starved second-instar larvae fed with pea leaves. Our results indicate that the predicted pathway can occur independently of the presence of plant myrosinases, because the same major glucosinolate-breakdown metabolites were found in the larvae feeding on treated watercress and pea leaves. A conjugation of glucosinolate-derived compounds with aspartic acid is a novel metabolic pathway that has not been described for other herbivores.
Publisher URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S096517482030120X
DOI: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2020.103431
Keeping up-to-date with research can feel impossible, with papers being published faster than you'll ever be able to read them. That's where Researcher comes in: we're simplifying discovery and making important discussions happen. With over 19,000 sources, including peer-reviewed journals, preprints, blogs, universities, podcasts and Live events across 10 research areas, you'll never miss what's important to you. It's like social media, but better. Oh, and we should mention - it's free.
Researcher displays publicly available abstracts and doesn’t host any full article content. If the content is open access, we will direct clicks from the abstracts to the publisher website and display the PDF copy on our platform. Clicks to view the full text will be directed to the publisher website, where only users with subscriptions or access through their institution are able to view the full article.


