Dietary Inflammatory Potential and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Among Men and Women in the U.S.
Background
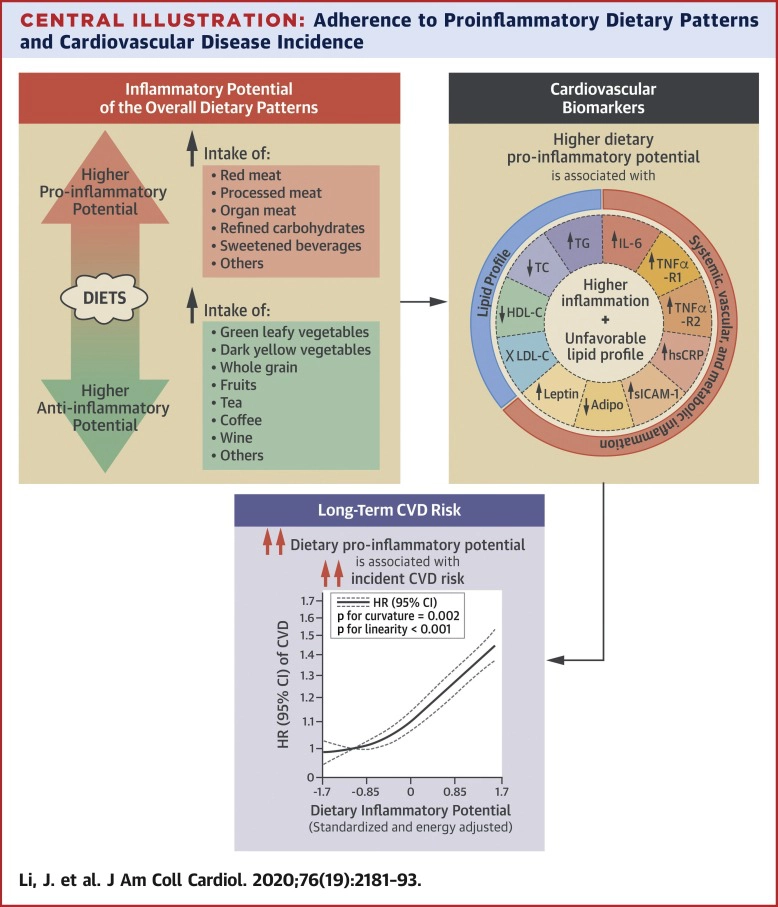
Inflammation plays an important role in cardiovascular disease (CVD) development. Diet modulates inflammation; however, it remains unknown whether dietary patterns with higher inflammatory potential are associated with long-term CVD risk.
Objectives
This study sought to examine whether proinflammatory diets are associated with increased CVD risk.
Methods
We prospectively followed 74,578 women from the Nurses' Health Study (NHS) (1984–2016), 91,656 women from the NHSII (1991–2015), and 43,911 men from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (1986–2016) who were free of CVD and cancer at baseline. Diet was assessed by food frequency questionnaires every 4 years. The inflammatory potential of diet was evaluated using a food-based empirical dietary inflammatory pattern (EDIP) score that was pre-defined based on levels of 3 systemic inflammatory biomarkers.
Results
During 5,291,518 person-years of follow-up, we documented 15,837 incident CVD cases, including 9,794 coronary heart disease (CHD) cases and 6,174 strokes. In pooled analyses of the 3 cohorts, after adjustment for use of anti-inflammatory medications and CVD risk factors including body mass index, a higher dietary inflammatory potential, as indicated by higher EDIP scores, was associated with an increased risk of CVD (hazard ratio [HR] comparing the highest to lowest quintiles: 1.38; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.31 to 1.46; p for trend <0.001), CHD (HR: 1.46; 95% CI: 1.36 to 1.56; p for trend <0.001), and stroke (HR: 1.28; 95% CI: 1.17- to 1.39; p for trend <0.001). These associations were consistent across cohorts and between sexes, and they remained significant after further adjustment for other dietary quality indices. In a subset of study participants (n = 33,719), a higher EDIP was associated with a higher circulating profile of proinflammatory biomarkers, lower levels of adiponectin, and an unfavorable blood lipid profile (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Dietary patterns with a higher proinflammatory potential were associated with higher CVD risk. Reducing the inflammatory potential of the diet may potentially provide an effective strategy for CVD prevention.
Publisher URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0735109720371904
DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.09.535
Keeping up-to-date with research can feel impossible, with papers being published faster than you'll ever be able to read them. That's where Researcher comes in: we're simplifying discovery and making important discussions happen. With over 19,000 sources, including peer-reviewed journals, preprints, blogs, universities, podcasts and Live events across 10 research areas, you'll never miss what's important to you. It's like social media, but better. Oh, and we should mention - it's free.
Researcher displays publicly available abstracts and doesn’t host any full article content. If the content is open access, we will direct clicks from the abstracts to the publisher website and display the PDF copy on our platform. Clicks to view the full text will be directed to the publisher website, where only users with subscriptions or access through their institution are able to view the full article.


